- Services
- Discovery & Intelligence Services
- Publication Support Services
- Sample Work

Publication Support Service
- Editing & Translation
-
Editing and Translation Services
- Sample Work

Editing and Translation Service
-
- Research Services
- Sample Work
Research Services
- Physician Writing
- Sample Work

Physician Writing Service
- Statistical Analyses
- Sample Work

Statistical Analyses
- Data Collection
- AI and ML Services
- Medical Writing
- Sample Work

Medical Writing
- Research Impact
- Sample Work

Research Impact
- Medical & Scientific Communication
- Medico Legal Services
- Educational Content
- Industries
- Subjects
- About Us
- Academy
- Insights
- Get in Touch
- Services
- Discovery & Intelligence Services
- Publication Support Services
- Sample Work

Publication Support Service
- Editing & Translation
-
Editing and Translation Services
- Sample Work

Editing and Translation Service
-
- Research Services
- Sample Work

Research Services
- Physician Writing
- Sample Work

Physician Writing Service
- Statistical Analyses
- Sample Work

Statistical Analyses
- Data Collection
- AI and ML Services
- Medical Writing
- Sample Work

Medical Writing
- Research Impact
- Sample Work

Research Impact
- Medical & Scientific Communication
- Medico Legal Services
- Educational Content
- Industries
- Subjects
- About Us
- Academy
- Insights
- Get in Touch

- Services
- Discovery & Intelligence Services
- Publication Support Services
- Sample Work

Publication Support Service
- Editing & Translation
-
Editing and Translation Services
- Sample Work

Editing and Translation Service
-
- Research Services
- Sample Work

Research Services
- Physician Writing
- Sample Work

Physician Writing Service
- Statistical Analyses
- Sample Work

Statistical Analyses
- Data Collection
- AI and ML Services
- Medical Writing
- Sample Work

Medical Writing
- Research Impact
- Sample Work

Research Impact
- Medical & Scientific Communication
- Medico Legal Services
- Educational Content
- Industries
- Subjects
- About Us
- Academy
- Insights
- Get in Touch

Systematic Literature Review Vs. Meta-Analysis: Understanding Evidence Synthesis
- Home
- Publication Support
- Journal Selection
- Systematic Literature Review Vs. Meta-Analysis: Understanding Evidence Synthesis
An Academy Guide
Interesting topics


Systematic Literature Review Vs. Meta-Analysis: Understanding Evidence Synthesis
A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a structured way of locating, appraising, and synthesizing all studies that are relevant to a specific research question in a way that is transparent, repeatable, and unbiased as achievable. A Meta-Analysis, however, is a statistical procedure for combining quantitative studies, located in an SLR, to provide an overall effect estimate. SLRs provide a broad summary of the evidence base, whereas meta-analyses summarize precisely, with a greater degree of confidence that can support evidence-based decision-making. [1]
1. What is a Systematic Literature Review?
A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a systematic way of identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing every piece of research evidence available. The SLR process is explicit and uses predetermined inclusion-exclusion criteria, which reduces the risk of bias typically associated with traditional literature reviews.
The SLR has a predetermined research question, encompasses an exhaustive and repeatable search of databases, an evaluation of articles included in the review, and data synthesis, and allows researchers to offer an evidence-based summary of the literature on a topic. This methodology is frequently used in healthcare, social sciences, and education for evidence-informed decisions and policy action. [2]
- Pre-identified research question.
- Exhaustive and repeatable search strategy.
- Critical appraisal of studies.
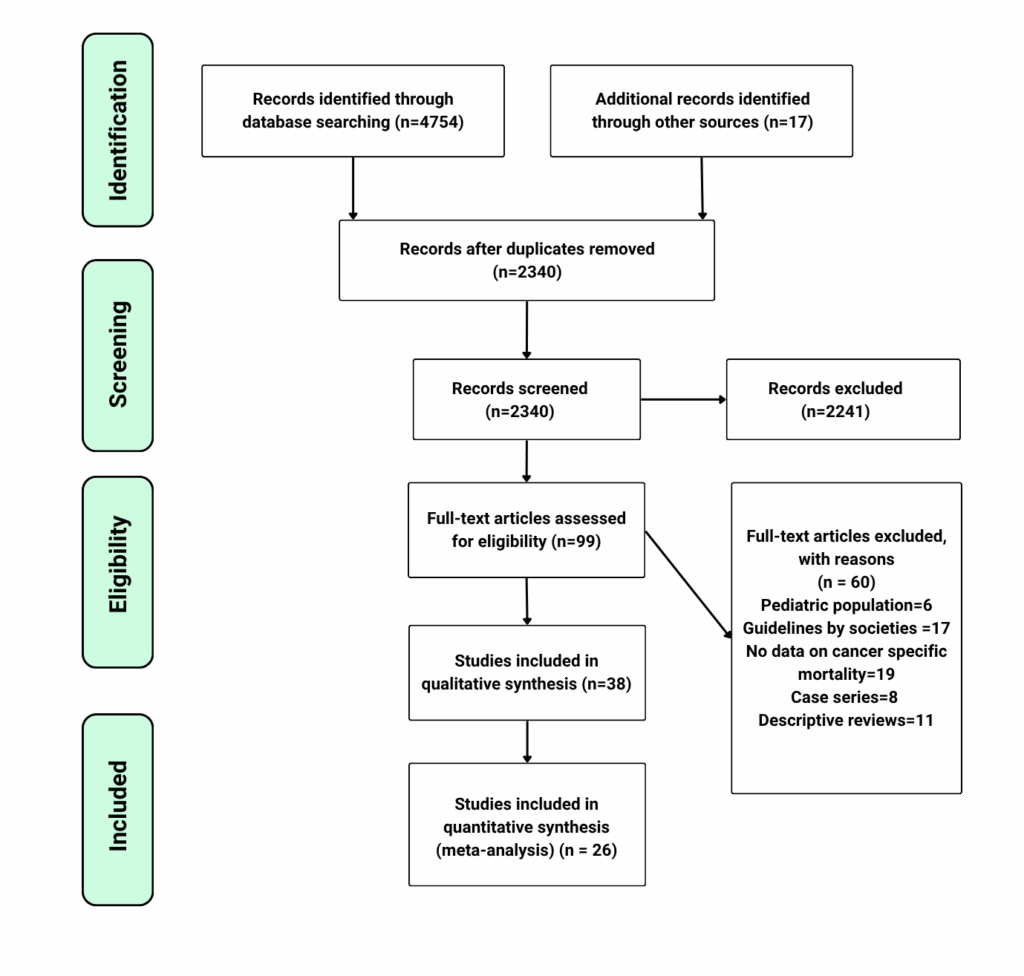
PRISMA flow diagram of the selection of studies to be included in the systematic review and meta-analysis
Measures the average number of citations received per article published in a journal over two years.[3]
2. What is a Meta-Analysis?
Meta-analysis is a statistical method that merges quantitative information across multiple studies to produce a combined effect size or relationship across studies. A meta-analysis is often completed in the context of a systematic review of the literature; however, the meta-analysis is primarily focused on the statistics rather than narrative synthesis. Meta-analyses help to statistically combine and analyze results, increase statistical power, reduce uncertainty, and provide a more accurate estimate of the true effect than a single study. [3]
- Quantitative synthesis
- Calculate effect sizes (e.g., odds ratios, differences in means)
- Assess heterogeneity across studies
3. Difference Between Systematic Literature Reviews and Meta-Analysis
Feature | Systematic Literature Review | Meta-Analysis |
Purpose | Summarize and critically appraise evidence | Combine quantitative results to estimate the overall effect |
Method | Narrative synthesis, thematic analysis | Statistical synthesis of data |
Data Type | Qualitative or quantitative | Quantitative |
Outcome | Comprehensive overview, identification of gaps | Precise numerical estimate of effect |
Bias Control | Through selection and appraisal criteria | Through statistical techniques and study weighting |
4. How to Perform a Systematic Literature Review
| Specify the Research Question |
|
| Create a Protocol |
|
| Conduct a Systematic Literature Search |
|
| Screen Studies |
|
| Assess Study Quality |
|
| Extract Data and Synthesize |
|
| Report Findings |
|
5. How to Access JCR?
JCR is available through Clarivate’s Web of Science platform. Access is typically provided through institutional subscriptions (universities, libraries, etc.). Individual researchers may also gain access through paid subscriptions or academic affiliations.
Conclusion
Meta-analysis and Systematic Literature Reviews form the cornerstone of evidence-based research. While a systematic literature review (SLR) will provide a rigorous and structured overview of the literature, a meta-analysis will pool the data and provide a more accurate estimate. Rigorous SLRs or meta-analyses provide reliability, reproducibility, and transparency, which ensure high-quality research and informed decisions.
Systematic Literature Review Vs. Meta-Analysis: Understanding evidence synthesis? Our Pubrica consultants are here to guide you. [Get Expert Publishing Support] or [Schedule a Free Consultation]
References
- Al-Khabori, M., & Rasool, W. (2022). Introduction to Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses of Therapeutic Studies. Oman medical journal, 37(5), e428. https://doi.org/10.5001/omj.2022.42
- Brignardello-Petersen, R., Santesso, N., & Guyatt, G. H. (2025). Systematic reviews of the literature: an introduction to current methods. American journal of epidemiology, 194(2), 536–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwae232
- Berman, N. G., & Parker, R. A. (2002). Meta-analysis: neither quick nor easy. BMC medical research methodology, 2, 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-2-10
- Khan, K. S., Kunz, R., Kleijnen, J., & Antes, G. (2003). Five steps to conducting a systematic review. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 96(3), 118–121. https://doi.org/10.1177/014107680309600304
- JABSOM Library. (2019, June 28). Systematic review toolbox. Hawaii.edu. https://hslib.jabsom.hawaii.edu/systematicreview/dataextraction