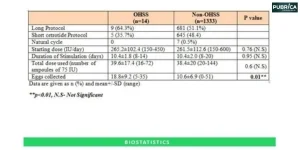
Endocrinology Research: Industry trends on Diabetes & Metabolism
The future of endocrinology is promising and has the potential to find innovative ways to mitigate the issues related to endocrine disorders such as diabetes and metabolic disorders
Trends in Diabetes & Metabolism
Similarly, robotic pills can deliver drugs directly to specific gastrointestinal sites, improve absorption, and reduce the side effects. These alternatives not only improve drug delivery and absorption in the body, but also reduce the burden of oral intake. In addition, there are many alternatives found in drug delivery such as smart insulin pens, microneedle patches, hydrogels, and implantable drug delivery devices. These technological innovations enhance the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of endocrine medications as well as improve patient adherence and quality of life.
Artificial pancreas system
Peptide-based drugs
Another milestone in peptide-based drug delivery is the NIPEP-TPP technology, enhancing therapeutic peptide delivery to specific tissues and oral routes. This technology utilizes cell-penetrating peptides to transport therapeutic drugs across cellular barriers, including the blood-brain barrier. It provides promising treatment solutions for central nervous system disorders and improves the efficacy of GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine, with the help of connected devices such as CGM (Continuous Glucose monitors), insulin pumps, and smart insulin pens can improve diabetes monitoring. It enables remote access and monitoring using data from EHR and other connected devices. Telemedicine models such as tele-education, nutrition, and psychology are filling the gaps in multidisciplinary support and collaboration in diabetes care.
Gene therapy
The studies related to genes are increasing in recent years, more innovations are occurring in treatment of diabetes. In one of recent studies, a specific variant of WSF1 gene, causing Wolfram syndrome has been identified in one of gene therapies . Although the studies can identify the variants and predict the risk of causing diabetes, it can be applied to all the populations in the world. Therefore, further studies are needed to explore more on the functions of genes and their association with the causing of diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Alternative therapies
Two insulin-independent therapies show promise in treating diabetes. Recombinant S100A9 treatment can inhibit ketogenesis, resulting in improved hyperglycemia without hypoglycemia while testing with mice. Teplizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, targets T cells by binding to CD3 and delays the onset of type 1 diabetes.
Future of endocrinology
Over the past decades, the field of endocrinology has shown significant progress, and it can be expected to progress in the coming years well. Further research in this field can help researchers and physicians find innovative treatment strategies and therapeutic agents to mitigate the effects of diseases and their causes. Finding novel therapeutic approaches that may change the endocrine system’s functioning may be made possible by having a thorough understanding of the system’s operations. It allows us to enhance treatment programs and patient results.
References
- Renzu, M., Hubers, C., Conway, K., Gibatova, V., Mehta, V. and Taha, W. (2024) Emerging technologies in endocrine drug delivery: innovations for improved patient care. Cureus, 16(6).
- https://www.news-medical.net/health/Future-of-Endocrinology.aspx
- https://endocrinenews.endocrine.org/category/practice/product-technology/
- Agarwal, S., Griffith, M.L., Murphy, E.J., Greenlee, C., Boord, J. and Gabbay, R.A. (2021) Innovations in diabetes care for a better “new normal” beyond COVID-19. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 106(1), pp.e377-e381.
- https://www.news-medical.net/health/Trailblazing-Discoveries-The-Top-5-Diabetes-Research-Breakthroughs-of-2023.aspx