- Services
- Discovery & Intelligence Services
- Publication Support Services
- Sample Work

Publication Support Service
- Editing & Translation
Editing and Translation Services
- Sample Work

Editing and Translation Service
- Research Services
- Sample Work
Research Services
- Physician Writing
- Sample Work

Physician Writing Service
- Statistical Analyses
- Sample Work

Statistical Analyses
- Data Collection
- AI and ML Services
- Research Impact
- Sample Work

Research Impact
- Medical & Scientific Communication
- Medico Legal Services
- Educational Content
- Industries
- Subjects
- About Us
- Academy
- Insights
- Get in Touch

- Services
- Discovery & Intelligence Services
- Publication Support Services
- Sample Work

Publication Support Service
- Editing & Translation
Editing and Translation Services
- Sample Work

Editing and Translation Service
- Research Services
- Sample Work

Research Services
- Physician Writing
- Sample Work

Physician Writing Service
- Statistical Analyses
- Sample Work

Statistical Analyses
- Data Collection
- AI and ML Services
- Research Impact
- Sample Work

Research Impact
- Medical & Scientific Communication
- Medico Legal Services
- Educational Content
- Industries
- Subjects
- About Us
- Academy
- Insights
- Get in Touch

What Are The Principles Of Experimental Design For Research
Experimental design, also referred to as “design of experiment,” is an area of applied statistics concerned with the preparation, execution, analysis, and interpretation of controlled testing. It is used to assess the variables that influence the value of a parameter or set of values. It is an effective data-gathering and analysis tool that may be used in a variety of experiments.
The technique of organizing an experiment to satisfy certain objectives is known as experimental design. Proper experiment planning is critical to ensuring that the appropriate type of data and sample size are available to answer research questions as clearly and effectively as feasible. Because of its capacity to neutralize the influence of confounding circumstances, the randomized controlled trial is still regarded as one of the top standards of research design in pharmacology.
⇒ Check our Examples to know more about how we research/review/edit research papers.
Experimental design is a crucial aspect of research in various fields, including science, social science, and engineering. The principles of experimental research design aim to ensure that experiments are conducted in a systematic review and controlled manner to produce reliable and valid results. Here are some key principles of experimental design:
- Clear Statement of Purpose: Define the research question or hypothesis that you want to investigate. What do you want to learn from the experiment?
- Control: Ensure that all variables, except for the one you’re testing, are held constant. This minimizes the influence of confounding variables on your results.
- Randomization: Randomly assign subjects or quasi-experimental design units to different treatment groups. This helps ensure that your results can be generalized to a larger population.
- Replication: Perform multiple trials or experiments to increase the reliability and generalizability of your results. This helps in assessing the consistency of the effects.
- Blocking: Group similar experimental study units together to account for potential sources of variation. This is particularly important in complex experiments.
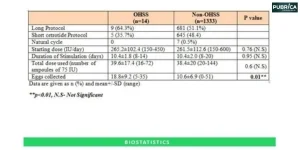
- Statistical Analysis: Use appropriate statistical methods to analyze your data. This helps determine the significance of the results and minimizes the impact of chance.
- Measurement and Data Collection: Ensure that your measurements are accurate and reliable. Use appropriate tools and techniques to collect data.
- Blinding and Double-Blinding: To reduce bias, researchers often use blinding (the subjects don’t know which treatment they’re receiving) and double-blinding (both the subjects and the experimenters don’t know) in experiments involving human participants.
These principles help ensure that the results of an experiment are both internally and externally valid, meaning that they accurately reflect the effects of the variables being studied and can be generalized to a broader population. Researchers often adapt and modify these principles to suit the specific needs and context of their experiments, but these principles provide a strong foundation for experimental design in statistics.
In conclusion, the fundamental principles of experimental design are pivotal in guiding the biomedical science research process. By formulating clear research objectives, maintaining stringent control over variables, employing randomization and replication, considering blocking, using appropriate statistical analysis, ensuring accurate data collection, and implementing blinding techniques when dealing with human subjects, researchers can enhance the quality and reliability of their experiments. These principles collectively foster the validity and generalizability of results, offering valuable insights into the phenomena under investigation. While the specifics of experimental design may vary depending on the field and research goals, these principles serve as a solid framework for robust and credible scientific inquiry.
⇒ Check our Blog for guidance on A Case Report of Type 1 Diabetes During the COVID-19 Vaccine.
Give yourself the academic edge today
Each order includes
- On-time delivery or your money back
- A fully qualified writer in your subject
- In-depth proofreading by our Quality Control Team
- 100% confidentiality, the work is never re-sold or published
- Standard 7-day amendment period
- A paper written to the standard ordered
- A detailed plagiarism report
- A comprehensive quality report