- Services
- Discovery & Intelligence Services
- Publication Support Services
- Sample Work

Publication Support Service
- Editing & Translation
Editing and Translation Services
- Sample Work

Editing and Translation Service
- Research Services
- Sample Work
Research Services
- Physician Writing
- Sample Work

Physician Writing Service
- Statistical Analyses
- Sample Work

Statistical Analyses
- Data Collection
- AI and ML Services
- Research Impact
- Sample Work

Research Impact
- Medical & Scientific Communication
- Medico Legal Services
- Educational Content
- Industries
- Subjects
- About Us
- Academy
- Insights
- Get in Touch

- Services
- Discovery & Intelligence Services
- Publication Support Services
- Sample Work

Publication Support Service
- Editing & Translation
Editing and Translation Services
- Sample Work

Editing and Translation Service
- Research Services
- Sample Work

Research Services
- Physician Writing
- Sample Work

Physician Writing Service
- Statistical Analyses
- Sample Work

Statistical Analyses
- Data Collection
- AI and ML Services
- Research Impact
- Sample Work

Research Impact
- Medical & Scientific Communication
- Medico Legal Services
- Educational Content
- Industries
- Subjects
- About Us
- Academy
- Insights
- Get in Touch

What is Epidemiological study design in meta-analysis research?
Epidemiological study design refers to the plan or structure that researchers follow when investigating the distribution and determinants of health-related events or conditions in a population. Public health epidemiology is crucial for understanding the patterns of diseases and their risk factors. Meta-analysis, on the other hand, is a statistical technique used to combine and analyze data from multiple studies to draw more robust conclusions than can be achieved from individual studies alone.
Check our Examples to know more how we research/review/edit research papers.
When conducting a meta-analysis in epidemiological research, researchers typically follow certain study design principles to ensure the reliability and validity of their findings. Here are some key aspects of epidemiological study design in the context of meta-analysis:
- Inclusion Criteria: Researchers must define clear inclusion criteria for selecting studies to be included in the meta-analysis. These criteria may include the types of participants, study designs, outcomes measured, and other relevant factors.
- Literature Search: A comprehensive and systematic literature search is conducted to identify all relevant studies. This involves searching databases, journals, conference proceedings, and other sources to locate both published and unpublished studies.
- Quality Assessment: The quality of each included study is assessed to evaluate its methodological rigour. This involves examining factors such as study design, sample size, data collection methods, and statistical analysis. Studies with low quality may be excluded or considered in sensitivity analyses.
- Data Extraction: Relevant data from each included study are extracted systematically. This includes information on study characteristics, participant demographics, exposure or intervention details, outcomes, and effect estimates.
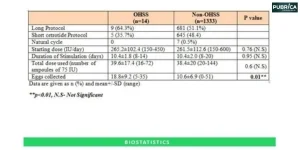
- Statistical Analysis: Meta-analysis involves the application of statistical techniques to combine the results of individual studies. Common measures include odds ratios, risk ratios, or mean differences, depending on the nature of the data. Genetic epidemiology, like Heterogeneity among studies, is also assessed.
- Publication Bias Assessment: Researchers need to evaluate the potential for publication bias, which occurs when studies with significant or positive results are more likely to be published than those with non-significant or negative results. Funnel plots and statistical tests may be employed to assess publication bias.
- Subgroup Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis: Subgroup analyses may be performed to explore potential sources of Heterogeneity, such as differences in study populations or methodologies. Sensitivity analyses are conducted to assess the robustness of the findings by testing the impact of excluding certain studies or changing analysis methods.
- Interpretation and Conclusions: The results of the meta-analysis are interpreted in the context of the included studies, considering their strengths and limitations. Conclusions drawn should be cautious and consider the overall evidence base.
Overall, careful consideration of these elements helps ensure that a meta-analysis in epidemiological research is conducted with rigour and provides valuable insights into the research question at hand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the application of rigorous epidemiological study design principles in meta-analysis in medical research is essential for deriving meaningful insights into the distribution and determinants of health-related events. By establishing clear inclusion criteria, conducting comprehensive literature searches, and systematically assessing the quality of included studies, research study design can enhance the reliability of their findings. The careful extraction and statistical synthesis of data, coupled with thorough assessments of Heterogeneity and potential biases, contribute to the robustness of meta-analytic results. Sensitivity analyses and subgroup examinations further refine interpretations. In the synthesis of evidence, Pubrica‘s nuanced understanding of study limitations is crucial, ensuring that conclusions drawn from meta-analyses in epidemiology reflect the strength of the overall evidence base.Top of Form
Check our Blog for guidance on A Case Report of Type 1 Diabetes During the COVID-19 Vaccine.
Related Topics:
☛ Systematic literature review writing services uk
Give yourself the academic edge today
Each order includes
- On-time delivery or your money back
- A fully qualified writer in your subject
- In-depth proofreading by our Quality Control Team
- 100% confidentiality, the work is never re-sold or published
- Standard 7-day amendment period
- A paper written to the standard ordered
- A detailed plagiarism report
- A comprehensive quality report