- Services
- Discovery & Intelligence Services
- Publication Support Services
- Sample Work

Publication Support Service
- Editing & Translation
Editing and Translation Services
- Sample Work

Editing and Translation Service
- Research Services
- Sample Work
Research Services
- Physician Writing
- Sample Work

Physician Writing Service
- Statistical Analyses
- Sample Work

Statistical Analyses
- Data Collection
- AI and ML Services
- Research Impact
- Sample Work

Research Impact
- Medical & Scientific Communication
- Medico Legal Services
- Educational Content
- Industries
- Subjects
- About Us
- Academy
- Insights
- Get in Touch

- Services
- Discovery & Intelligence Services
- Publication Support Services
- Sample Work

Publication Support Service
- Editing & Translation
Editing and Translation Services
- Sample Work

Editing and Translation Service
- Research Services
- Sample Work

Research Services
- Physician Writing
- Sample Work

Physician Writing Service
- Statistical Analyses
- Sample Work

Statistical Analyses
- Data Collection
- AI and ML Services
- Research Impact
- Sample Work

Research Impact
- Medical & Scientific Communication
- Medico Legal Services
- Educational Content
- Industries
- Subjects
- About Us
- Academy
- Insights
- Get in Touch

How to do a meta-analysis for a manuscript?
Meta-analysis is a crucial method for knowledge accumulation in various scientific fields, serving as a synopsis of research questions or fields. It provides a quantitative assessment of the relationship between target variables or intervention effectiveness, tests competing theoretical assumptions, and identifies important moderators. Originating in the 1970s, meta-analysis is now an established method in management research and related fields. It can test competing assumptions or identify moderators in different primary studies.
❖ Check our Blog for guidance on Ten simple rules for carrying out and writing meta-analysis.
Performing a meta-analysis for a manuscript involves several steps to ensure the process is conducted accurately and transparently. Here’s a general guide on how to conduct a meta-analysis for a manuscript:
- Research Question and Protocol: Clearly define your research question or objective. Specify the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the studies you intend to include in the meta-analysis. Develop a protocol outlining the study design, data sources, search strategy, and statistical methods you will use. This will help ensure transparency and prevent bias during the process.
- Literature Search: Conduct a comprehensive literature search to identify relevant studies. Search electronic databases (e.g., PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus) using relevant keywords and MeSH terms. Additionally, check reference lists of relevant articles and review papers to find additional studies.
- Study Selection: Screen the identified studies based on your pre-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Assess each study’s relevance and quality. This process should involve multiple reviewers to ensure consistency and minimize bias.
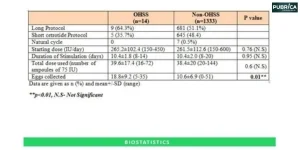
- Data Extraction: Extract relevant data from the selected studies. Commonly extracted data include study characteristics (e.g., author, publication year, location), participant characteristics (e.g., sample size, demographics), intervention/exposure details, outcome measures, effect sizes (e.g., odds ratios, means, hazard ratios), and associated uncertainty (e.g., confidence intervals, standard errors).
- Data Synthesis and Analysis: Use statistical software (e.g., R, Stata, or specialized meta-analysis software like RevMan) to conduct the meta-analysis. Depending on the nature of the data and the included studies, you may use fixed- or random-effect models to estimate pooled effect sizes and associated measures of uncertainty (e.g., 95% confidence intervals).
- Assess Heterogeneity: Examine the included studies for heterogeneity to assess the degree of variance in effect sizes above what would be anticipated by chance. This may be accomplished through the use of statistical tests such as Cochran’s Q and I^2 statistics.
- Subgroup and Sensitivity Analyses: If significant heterogeneity is present, conduct subgroup analyses to explore potential sources of heterogeneity (e.g., study design, participant characteristics, intervention/exposure variations). Additionally, perform sensitivity analyses to evaluate the robustness of your results by excluding studies with specific characteristics or varying meta-analysis research approaches.
- Publication Bias Assessment: Assess publication bias, which is the tendency for studies with statistically significant results to be published more often than those with non-significant results. This can be done using funnel plots or statistical tests (e.g., Egger’s test).
- Interpretation of Results: Interpret the results of your meta-analysis in the context of the research question and the included studies. Discuss the implications of the findings and potential limitations of the meta-analysis.
- Manuscript Writing: Write the meta-analysis manuscript following the standard structure of a scientific paper, including an introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion sections. Be sure to present the meta-analysis results clearly and provide sufficient details for readers to understand the process.
- Peer Review and Revision: Submit the manuscript writing to a reputable journal for peer review. Address any reviewer comments and suggestions and, if necessary, revise the manuscript review services accordingly.
Remember that conducting a meta-analysis requires a solid understanding of statistical methods and data analysis. If you are unfamiliar with these techniques, consider collaborating with a statistician or methodologist during the process. Additionally, adhering to guidelines like PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) can enhance the quality and transparency of your meta-analysis.
❖ Check our meta-analysis sample work to know and learn more about “A meta-analysis of the relationship between Helicobacter Pylori infection and ABO blood groups.”
A meta-analysis is crucial for researchers to synthesize evidence from multiple studies and draw meaningful conclusions on a research question. It ensures reliability and validity by following a well-defined protocol and adhering to transparent procedures. The process involves a comprehensive literature search, stringent study selection, data extraction, synthesis, heterogeneity assessment, subgroup and sensitivity analyses, and publication bias evaluation. The meta-analysis presents a comprehensive narrative, offering insights and implications contributing to existing knowledge. Pubrica services adhere to reporting guidelines and maintain clarity; the meta-analysis is a powerful tool for synthesizing evidence, establishing trends, and identifying key patterns, advancing our understanding of complex phenomena and informing future research and decision-making processes.
Give yourself the academic edge today
Each order includes
- On-time delivery or your money back
- A fully qualified writer in your subject
- In-depth proofreading by our Quality Control Team
- 100% confidentiality, the work is never re-sold or published
- Standard 7-day amendment period
- A paper written to the standard ordered
- A detailed plagiarism report
- A comprehensive quality report