What is a meta-analysis in Cochrane Reviews?
What Is Publication Bias In A Systematic Review?
Cochrane Reviews base their conclusions on the findings of research that fulfil particular quality standards because the most trustworthy studies will give the best evidence for making healthcare decisions. Cochrane Review authors use strategies to minimize the influence of bias throughout the review process, including:
- Identifying relevant research from a variety of sources (including unpublished sources);
- Selection of studies for inclusion and assessment of their strengths and weaknesses using established criteria.
- Data gathering is systematic.
- Data synthesis is appropriate.
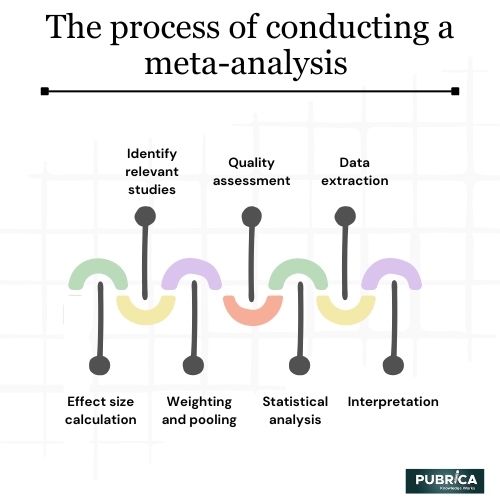
- Identify relevant studies: The researchers perform a comprehensive search to identify all the relevant studies that meet specific inclusion criteria.
- Quality assessment: Each included study is critically appraised to assess its methodological quality and risk of bias. This step is crucial to determine the reliability and validity of the individual study's results.
- Data extraction: The relevant data from each study are extracted, including sample sizes, effect sizes, and measures of variability.
- Effect size calculation: For each study, an effect size is calculated based on the outcome of interest (e.g., the difference in means between treatment groups). Effect sizes are standardized metrics that allow for comparison across different studies.
- Weighting and pooling: The effect sizes from individual studies are combined, giving more weight to larger studies and those with more robust methodology. This pooling process yields an overall effect size representing the average treatment effect across all included studies.
- Statistical analysis: Statistical techniques are used to assess the heterogeneity among the individual study results and calculate the overall effect size and confidence interval. The confidence interval helps estimate the precision of the effect size.
- Interpretation: The findings of the meta-analysis are interpreted, taking into account the overall treatment effect, its uncertainty, and the potential implications for clinical practice or policy.
The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions and the Cochrane Handbook for Diagnostic Test Accuracy Reviews go into great length on these methodologies.
Because the findings of new research might modify the conclusions of a review, Cochrane Reviews are updated to reflect the findings of new information as it becomes available. Cochrane Reviews are thus useful resources for people receiving and delivering care, decision-makers, and researchers.
Meta-analysis in Cochrane Reviews is a statistical technique used to combine and analyze the results from multiple studies that have investigated the same or similar research question. Cochrane Reviews are systematic reviews conducted by the Cochrane Collaboration, an international network of researchers, healthcare professionals, and other stakeholders, to provide evidence-based information to guide healthcare decisions.
A systematic review involves systematically searching, selecting, appraising, and synthesizing all available evidence on a specific topic to answer a well-defined research question. If the included studies are similar enough in terms of their design, interventions, and outcomes, a meta-analysis can be conducted to pool the data and obtain a more precise estimate of the treatment effect or outcome of interest.
The process of conducting a meta-analysis typically involves the following steps:
Meta-analysis research in Cochrane Reviews is valuable because it provides a more comprehensive and precise estimate of the treatment effect or outcome, increasing the statistical power and reliability of the results. However, ensuring that the included studies are sufficiently similar and well-conducted is essential to produce valid and meaningful conclusions. If substantial heterogeneity exists among the studies, it may limit the ability to pool the data, and the researchers may need to explore the reasons behind the variability and consider alternative approaches for synthesis.
Give yourself the Medical edge today
Each order includes
- On-time delivery or your money back
- A fully qualified writer in your subject
- In-depth proofreading by our Quality Control Team
- 100% confidentiality, the work is never re-sold or published
- Standard 7-day amendment period
- A paper written to the standard ordered
- A detailed plagiarism report
- A comprehensive quality report

