
List the five mistakes that may happen while writing an effective literature review for biomedical research dissertation
July 29, 2020
Do’s and Don’ts in writing a scientific literature review for health care research
August 18, 2020Blockchain is the system of recording information in such a way that makes it impossible or difficult to either change, hack or cheat the system. It is a structure which stores transactional records of the public in various databases. The transitional records are known as “block”, while the databases are known as “chain”. This system involves a network that is connected through peer to peer nodes. Within these nodes, the blockchains are stored. In other words, the nodes are actually computers within a system where the data is being stored. Each node saves a copy the transactions.
How datablocks form a blockchain can be illustrated with the image given below:
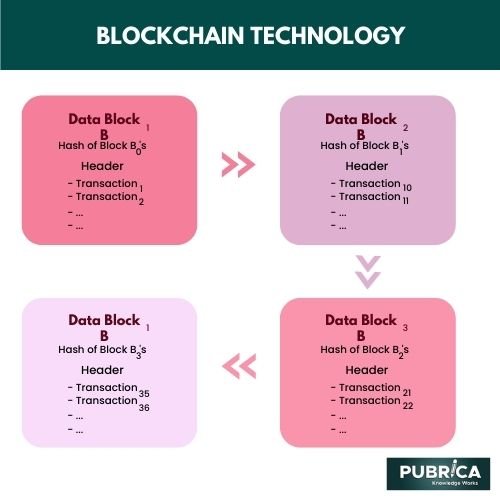
Healthcare workers and scientists in the biomedical field have been using blockchain technology for data sharing. The domains in healthcare system who use this technology include drug development, consumer health, medical research, supply chain management, data security, etc.
In healthcare, blockchain technology allows accession rules for a particular set of medical data. Researchers can access parts of data for a fixed time interval. Patients can also access the database of hospitals for an automated collection of medical data. Even in the field of literature research, blockchain technology is applicable in a similar manner. Researchers can have access to a centralized database containing published research data, but for a limited period of time or for specific research articles.
Evidence based Clinical literature review services :
A clinical literature review can be described as an informative and critically written document on a chosen topic. There are three categories of evidence based Medical Literature Review Writing Services, namely initial consultation, search services and post search services.
Initial consultation involves providing guidance, checking the type of document, assist in developing protocols for the systematic review and advicing the use of a software. Search services include conducting researches of PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase and Cochrane databases, exporting the results of database search to a citation management tool and maintaining copies of documentations. Post search services include making a draft of the methods section within literature search, guiding on screening of citations and assisting in editing and submission of publication.
Plagiarism and its correction:
Plagiarism may be defined as the practice of copying someone else’s ideas or work and exhibiting them as one’s own. It is essential that any systematic review is absolutely free of plagiarism. Blockchain technology has an important role to play in checking plagiarism as well. The technology follows certain principles which are helpful to prevent a researcher from copying other’s work. The table below gives those details.
| Blockchain principle | Details |
| Distributed database | A single member does not have control over data. Each member can verify transactions without any intermediate person |
| Peer-to-peer transmission | There is no central authority. Members can directly communicate with each other |
| Transparency with pseudonymity | Each transaction is visible to any other person who has an access to the blockchain |
| Irreversibility of records | Records cannot be altered once a transaction has been entered |
| Computational logic | Blockchain transactions can be programmed |
The reviewer and the researcher can be a part of the same blockchain. In this way, the reviewer will be able to keep a tab on the researcher’s access to different literatures. This will give the reviewer an idea which articles the researcher is accessing . A reviewer runs a paper through a plagiarism detector when discrepancies in few factors are found. These include:
- Style/Voice: Reviewers are familiar with different styles and formats of writing. If the reworked literature has a completely different style of writing not present in the previous works, then probably the student has copied someone else’s work.
- Inconsistency: This includes changes in the type of font, font size and formatting of text that indicate copying and pasting of information from some other literature work. In case the doubtful passages do not have quotations or are without any citations, then it is obvious that the literature is plagiarized.
- Old References: In case very old and outdated references are used by a researcher then it is suggestive to the reviewer that the researcher is trying to recycle some other researcher’s work.
Applications of blockchain technology in healthcare and biomedical sciences
Blockchain technology has the potential for maintaining a secured sharing of patient records throughout his/her lifetime. There are three key elements that need to be considered while developing a blockchain for biomedical field and they are scalability, security of data access and maintenance of data privacy. The table given below shows in which all ways blockchain technology is beneficial for the healthcare system.
| Feature of the blockchain | Advantages in healthcare and biomedical research |
| Peer-to-peer networks | Security of network infrastructure |
| Smart contracts | Permissions needed to access patient data |
| Closed network | Integrity of data |
| Transaction disintermediated | Reduction in transaction costs |
| Real time updates shared with every member | Collaboration |
| Cryptography | Patient’s identity is protected |
| Distributed framework | Exchange of health information |
In a systematic review on blockchain technology conducted by C. Agbo et.al. in 2020, several benefits of blockchain to healthcare applications have been cited. These are discussed:
- Blockchain can act as a decentralized health data management backbone from wherein all stakeholders can have a controlled access to the same health records.
- Data once saved to the blockchain, cannot be corrupted, altered or retrieved. The data are encrypted, time-stamped and appended following a chronology. This helps in an improved data security and protection of the privacy and identity of the patient.
- Blockchain helps the patients to own a data and gives the assurance that their health records are not misused by others.
- The blockchain system is robust and resilient against loss of data, corruption of data and security attacks on availability of data.
- Blockchain has an open and transparent nature. This creates trust among healthcare professionals.
- Blockchain facilitates verifiability of data in areas such as pharmaceutical supply chain management and insurance claim processing.
References:
- Justinia T. Blockchain Technologies: Opportunities for Solving Real-World Problems in Healthcare and Biomedical Sciences. Acta Inform Med. 2019 Dec, 27(4):284-291. doi: 10.5455/aim.2019.27.284-291. PMID: 32055097; PMCID: PMC7004292.
- Yoon HJ. Blockchain Technology and Healthcare. Healthc Inform Res. 2019 Apr, 25(2):59-60. doi: 10.4258/hir.2019.25.2.59. Epub 2019 Apr 30. PMID: 31131139; PMCID: PMC6517629.
- Agbo, Cc & Mahmoud, Qusay & Eklund, J., (2019). Blockchain Technology in Healthcare: A Systematic Review. Healthcare. 7. 56. 10.3390/healthcare7020056.
