Targeted literature searches are a fundamental part of writing clinical manuscripts that will meet the standards of high-quality journals and contribute meaningfully to evidence-based practice. When physicians write clinical manuscripts, utilizing a targeted literature search can identify high-quality, relevant, and current evidence. While a general literature review is useful, a targeted literature search is specific to the clinical question and should be completed through frameworks established, such as PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome) and PRISMA [1].
How Can Researchers Avoid Plagiarism While Ensuring the Originality of Their Manuscript?
- Home
- Academy
- Research Impact
- How Can Researchers Avoid Plagiarism While Ensuring the Originality of Their Manuscript?
High-Impact Journals
Interesting topics
How Can Researchers Avoid Plagiarism While Ensuring the Originality of Their Manuscript?
Plagiarism poses a serious challenge to the credibility and trustworthiness of research within the academic community. It is therefore the responsibility of all researchers to take intentional action to protect their work and to ensure originality and authenticity. First, they must learn what plagiarism is and adopt appropriate citation practices. Once they are familiar with that, they need to use plagiarism checker tools to verify their work.[1]
1. Understanding Plagiarism
Plagiarism can be defined as the use of someone else’s work, ideas, or intellectual property without providing proper attribution, a process that makes the ideas or work seem one’s own. Plagiarism can include: [2]
- Order-taking: Taking material word-for-word from a source, without citation.
- Paraphrasing: Restating the ideas of another person without proper attribution, even if stated in your words.
- Self-plagiarism: Taking one’s previous work without citations [3]
- Fraudulent citation: Citing a source that was not used or cited incorrectly.
Researchers must make every effort they can to correctly cite every source of information and idea they use in their work, even if they are simply paraphrasing the ideas. Using a plagiarism checker for a research paper is essential to ensure all sources are properly credited.
2. How to Write a Research Paper Without Plagiarism
Maintaining academic integrity is fundamental when preparing a manuscript for peer-reviewed publication. Plagiarism—intentional or accidental—can lead to rejection or retraction. The following best practices will help ensure your paper remains original and ethically sound:
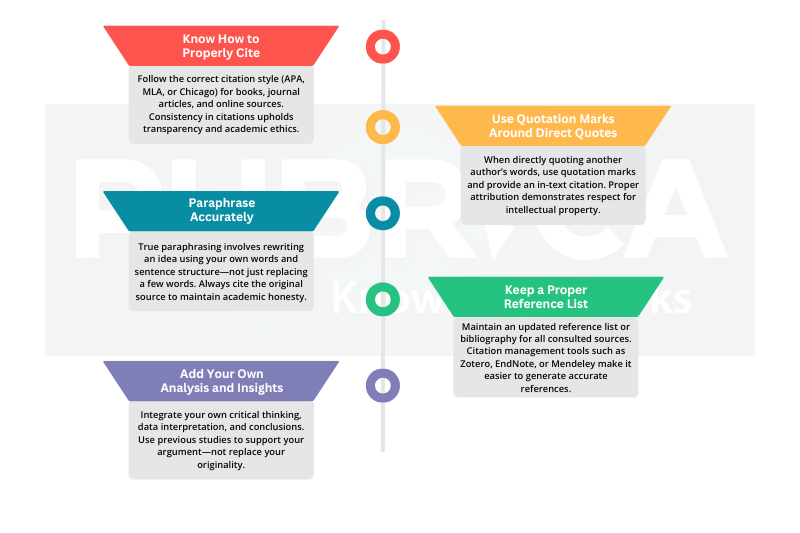
- Know How to Properly Cite
Follow the correct citation style (APA, MLA, or Chicago) for books, journal articles, and online sources. Consistency in citations upholds transparency and academic ethics. - Use Quotation Marks Around Direct Quotes
When directly quoting another author’s words, use quotation marks and provide an in-text citation. Proper attribution demonstrates respect for intellectual property. - Paraphrase Accurately
True paraphrasing involves rewriting an idea using your own words and sentence structure—not just replacing a few words. Always cite the original source to maintain academic honesty. - Keep a Proper Reference List
Maintain an updated reference list or bibliography for all consulted sources. Citation management tools such as Zotero, EndNote, or Mendeley make it easier to generate accurate references. - Add Your Own Analysis and Insights
Integrate your own critical thinking, data interpretation, and conclusions. Use previous studies to support your argument—not replace your originality. - Plan and Draft Early
Allocate sufficient time for writing, revising, and proofreading. Well-planned writing reduces dependence on others’ wording and helps ensure original research output.
Finally, before journal submission, use a plagiarism checker for scientific papers such as iThenticate or Turnitin to verify your similarity index and confirm compliance with research ethics and peer-review standards [4].
3. How to Use an Online Plagiarism Checker
Before submitting your research paper or journal manuscript, it is crucial to verify its originality using a reliable plagiarism checker. These tools help identify duplicated phrases, missing citations, or paraphrased sections that may raise your similarity index.
Tool | Features | Strengths | Limitations |
Turnitin | Compares text with academic journals, research papers, and student submissions | Industry standard in academic institutions; provides detailed similarity reports | Paid subscription required |
Grammarly | Checks grammar, style, and plagiarism | User-friendly; integrates with writing tools; affordable for individuals | Limited coverage of academic databases |
Quetext | Performs deep plagiarism searches with citation assistance | Free version available; generates similarity percentage | Free tier has limited word count and features |
Copyscape | Compares online content for plagiarism | Ideal for blogs and website content | Not suited for scholarly or research manuscripts |
When preparing a journal article submission, always choose a plagiarism checker designed for academic writing. Tools like Turnitin or iThenticate (journal plagiarism checker) compare your manuscript against millions of published research papers, theses, and conference proceedings providing a clear plagiarism report to help you maintain academic integrity and avoid unintentional overlap.
4. Does Similarity Always Indicate Plagiarism?
No, similarity does not always mean plagiarism. In academic and research writing, a certain level of similarity index is normal and acceptable. Tools like Turnitin or other AI plagiarism detection software often flag repeated phrases, technical terms, or references that do not actually indicate copied content.
|
Common Phrases and Terminology In highly specialized fields, repeating technical terms or standardized phrases is acceptable and does not count as plagiarism. For example, phrases such as “the theory of relativity” or “statistical significance level of 0.05” are standard in scientific writing. |
Widely Accepted Facts Facts or general knowledge—like “The Earth orbits the Sun”—are considered common knowledge and do not require citation. Only when you use another author’s unique wording or interpretation should you cite the source. |
|
Quotation Direct quotations will appear in a similarity report, but when properly cited and enclosed in quotation marks, they are not plagiarism. Always attribute quotes to their original source to maintain academic integrity. |
References A high similarity in the reference list is not plagiarism; all academic papers follow standard citation formats (APA, MLA, or Vancouver). Still, using a journal plagiarism checker helps ensure your research paper maintains originality and complies with publication ethics. |
5. Takeaway
To keep your research paper original and plagiarism-free, you should:
- Credit sources appropriately every time, even if paraphrased.
- Make use of any reference checking tool as a second line of protection, such as a plagiarism check report service.
- Remember that similarity does not always indicate plagiarism, particularly with common terms, quotes, or facts.
Using a plagiarism check service ensures that no part of your work is unintentionally duplicated from another source.
Connect with us to explore how we can support you in maintaining academic integrity and enhancing the visibility of your research across the world!
Conclusion
Researchers are an important part of the academic integrity process. Scholars can ensure newness in their manuscripts by understanding plagiarism and learning best practices to cite sources, paraphrase, and locate and use plagiarism checkers. Although plagiarism checkers provide a similarity score, they can only sometimes determine plagiarism and require thorough consideration to determine the best course of action.
How Can Researchers Avoid Plagiarism While Ensuring the Originality of Their Manuscript? Our Pubrica consultants are here to guide you. [Get Expert Publishing Support] or [Schedule a Free Consultation]
References
- Yadav, S.K. (2023). Referencing and Avoiding Plagiarism. In: Research and Publication Ethics. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26971-4_11
- Taylor, J.S. Reassessing Academic Plagiarism. J Acad Ethics22, 211–230 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10805-023-09478-4
- Oviedo-García, M.Á. The review mills, not just (self-)plagiarism in review reports, but a step further. Scientometrics129, 5805–5813 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-024-05125-w
- Kumar, P. M., Priya, N. S., Musalaiah, S., & Nagasree, M. (2014). Knowing and avoiding plagiarism during scientific writing. Annals of medical and health sciences research, 4(Suppl 3), S193–S198. https://doi.org/10.4103/2141-9248.141957
