Targeted literature searches are a fundamental part of writing clinical manuscripts that will meet the standards of high-quality journals and contribute meaningfully to evidence-based practice. When physicians write clinical manuscripts, utilizing a targeted literature search can identify high-quality, relevant, and current evidence. While a general literature review is useful, a targeted literature search is specific to the clinical question and should be completed through frameworks established, such as PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome) and PRISMA [1].
What is the importance of a literature review in research?
- Home
- Academy
- Research Impact
- What is the importance of a literature review in research?
High-Impact Journals
Interesting topics
What is the importance of a literature review in research?
The literature review is a foundational aspect of any research project, thesis, or dissertation. It is the systematic review and synthesis of existing literature on your research topic. As research becomes increasingly data-driven and more interdisciplinary across disciplines, the need for an accurate literature review is greater than ever. [1] A literature review is an important component of research, as it ensures that the new research is building on what is known, identifying gaps in the literature, and contributing to the academic community.
This article explores the importance, functions, and evolving trends of literature reviews in modern research, with practical insights into how they shape academic integrity and innovation, and successful scientific manuscript publication. [2]
1. Understanding the Concept of a Literature Review
A literature review is a systematic, critical evaluation of scholarly information (e.g., scientific papers, books, theses, reports) on a particular topic or research question. It is not just a summary of studies but rather a synthesis that demonstrates the researcher’s comprehension of recent trends, approaches, and controversies in a discipline. In other words, it establishes a research project within the academic discourse and justifies why the research is necessary.
2. Types of Literature Reviews
Types of Literature Reviews | Description |
Narrative Review [3] | Summarizes previous studies to build a general understanding. |
Systematic Review [4] | Uses a structured and transparent method to collect and analyze data from studies. |
Meta-analysis [5] | Combines statistical results from multiple studies to identify overall trends. |
Scoping Review [6] | Maps key concepts and research gaps in a broad area. |
3. Importance of a Literature Review in the Research
The importance of literature review in scientific manuscripts can be condensed into an analytical feature to enable the multifold reach of its significance. It adds value to the legitimacy of the research in many ways:
- Provides the interpretation of existing literature in light of updated developments in the field to help in establishing the consistency in knowledge and relevance of existing materials
- It helps in calculating the impact of the latest information in the field by mapping their progress of knowledge.
- It brings out the dialects of contradictions between various thoughts within the field to establish facts
- The research gapsscrutinized initially are further explored to establish the latest facts of theories to add value to the field
- Indicates the current research place in the schema of a particular field
- Provides information for relevancy and coherence to check the research
- Apart from elucidating the continuance of knowledge, it also points out areas that require further investigation and thus aid as a starting point for any future research
- Justifies the research and sets up the research question
- Sets up a theoretical framework comprising the concepts and theories of the research upon which its success can be judged
- Helps to adopt a more appropriate methodology for the research by examining the strengths and weaknesses of existing research in the same field
- Increases the significance of the results by comparing them with the existing literature
- Provides a point of reference by writing the findings in the scientific manuscript
- Helps to get the due credit from the audience for having done the fact-finding and fact-checking mission in the scientific manuscripts
- The more references to relevant sources, of it could increase more of its trustworthiness with the readers
- Helps to prevent plagiarism by tailoring and uniquely tweaking the scientific manuscript not repeat others’ original ideas
- By preventing plagiarism, it saves the scientific manuscript from rejection and thus also saves a lot of time and money
- Helps to evaluate, condense, and synthesize the gist in the author’s own words to sharpen the research focus
- Helps to compare and contrast to show the originality and uniqueness of the research than that of existing other research
- Rationalizes the need for conducting the particular research in a specified field
- Helps to collect data accurately to allow for any new methodology of research beyond the existing ones
4. Sources of Literature Review
Effective writing a literature review depends on high-quality, credible sources such as:
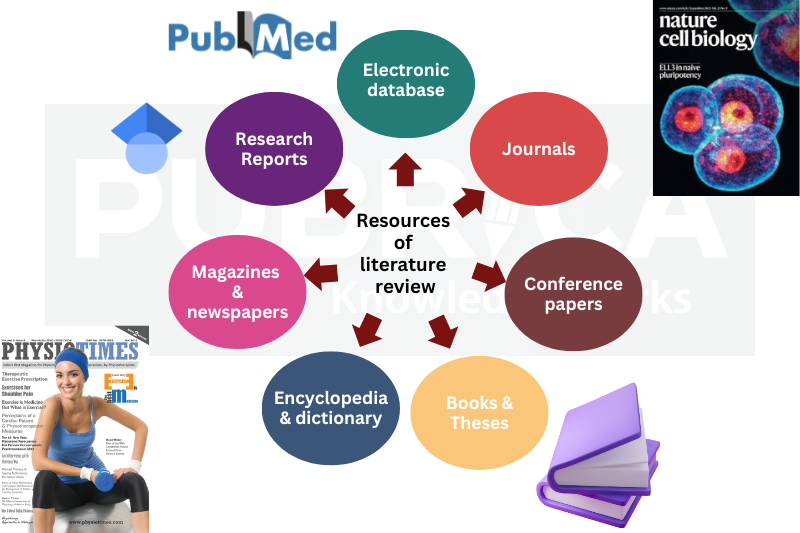
5. Modern Trends in Literature Reviews
The practice of conducting literature reviews has evolved significantly due to technological advances and the growing volume of scholarly output. Several key trends define how researchers approach literature reviews:
Trend | Description | Example |
AI-Assisted Literature Analysis | Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools like Scite.ai, Elicit, and Semantic Scholar help identify patterns, citation networks, and research gaps automatically. | AI-driven keyword mapping identifies underexplored topics in cancer genomics. |
Systematic and Scoping Reviews | Structured approaches (like PRISMA) ensure transparency and reproducibility, especially in healthcare and social sciences. [7] | Systematic reviews are now mandatory for most clinical research proposals. |
Integration of Bibliometric Analysis | Researchers use citation metrics to measure the influence of publications and emerging trends. | Visualization tools such as VOSviewer show keyword co-occurrence maps. |
Interdisciplinary Literature Reviews | The boundaries between disciplines are blurring, prompting cross-domain analysis. | Studies on climate change combine environmental science, economics, and sociology. |
Open Access and Digital Databases | Access to vast open-access journals and repositories enables global inclusivity in research. | Databases like PubMed Central and DOAJ offer free access to peer-reviewed literature. |
Connect with us to explore how we can support you in maintaining academic integrity and enhancing the visibility of your research across the world!
Conclusion
Conducting a comprehensive literature review remains one of the most critical and value-adding steps in research. It anchors new studies within the existing body of knowledge, clarifies theoretical and methodological directions, and ensures intellectual honesty. As research ecosystems grow more digital and interconnected, literature reviews serve as the intellectual bridge between past scholarship and future discovery. [8]
A well-executed literature review not only strengthens the quality of research but also ensures that every scholarly effort contributes meaningfully to collective human knowledge.
Why is it important to do a literature review in research?. Our Pubrica consultants are here to guide you. [Get Expert Publishing Support] or [Schedule a Free Consultation]
References
- Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 104, 333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039
- Boote, D. N., & Beile, P. (2005). Scholars before researchers: On the centrality of the dissertation literature review in research preparation. Educational Researcher (Washington, D.C.: 1972), 34(6), 3–15. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189×034006003
- Laghlam, D., Benghanem, S., Ortuno, S., Bouabdallaoui, N., Manzo-Silberman, S., Hamzaoui, O., & Aissaoui, N. (2024). Management of cardiogenic shock: a narrative review. Annals of Intensive Care, 14(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-024-01260-y
- Abdi, A., Jalilian, M., Sarbarzeh, P. A., & Vlaisavljevic, Z. (2020). Diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review on the current evidences. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 166(108347), 108347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108347
- Gonçalves, D. L. N., Moreira, T. R., & da Silva, L. S. (2022). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between uric acid levels and chronic kidney disease. Scientific reports, 12(1), 6251. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-10118-x
- Poo, C. L., Lau, M. S., Nasir, N. L. M., Nik Zainuddin, N. A. S., Rahman, M. R. A. A., Mustapha Kamal, S. K., Awang, N., & Muhammad, H. (2024). A Scoping Review on Hepatoprotective Mechanism of Herbal Preparations through Gut Microbiota Modulation. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(10), 11460-11502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46100682
- Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., … Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.), 372, n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
- Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
