The restrictions and processes of grant review decision-making, as well as their effects on the outcome
Research councils use peer review to ensure that only the best projects receive funding. The things that assessors prioritize and how they do so may differ greatly since there are no standardized evaluation norms. Therefore, the factors affecting peer review may be coincidental in that who analyzes which study and how ideas are organized may impact the conclusion. This article looks at how the review procedure affects the results of grant reviews. The Research Council of Norway’s processes is examined in the case study because it employs a range of grant-review techniques and is thus ideally suited to researching the effects of different models. Direct observation of panel discussions, panel member interviews, and research are the main sources of data. According to one unfavorable study, rating scales and financial restrictions are more pertinent than review regulations for the criteria employed by the reviewers. The methods used by the review panels to decide how to rank proposals have greatly influenced the result. While some ranking methodologies favor safe and uncontroversial endeavors, others favor intellectual variety and contentious research.
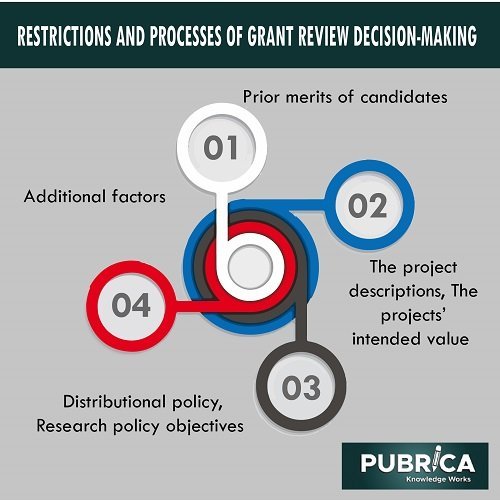
The study’s important categories included the ranking views and the assessment criteria (with examples of the criteria and justifications in brackets).
- the project descriptions (methods, clarity, novelty, and relevance); • the earlier accomplishments of applicants (publications, citations, originality, solidity, research experience);
- the desired value of the undertaking (scholarly or scientific merit, anticipated application or applicability for narrow or broad audiences);
- distributional guidelines (research area, organization, setting, and gender);
- the goals of research policy (developing research expertise in certain disciplines/’needs’ of the regions, [big] multidisciplinary initiatives, international collaboration, scholarly breadth/pluralism/diversity, and the field’s national significance);
- other variables (budget and budgetary duties, budget optimization for the panel, prior or further funds obtained by the applicant).
Author’s Update: Keep up to date on industry advancements, support, and training.
Pubrica Connect: Read articles about research, technology, and health communities daily.
Researcher Academy:Improve your manuscript by learning academic writing skills.
Language editing by Pubrica Author Services:Before submitting your work, double-check that it is written in proper English.
Translation by Pubrica Author Services: Translate your work into English professionally.
Search engine optimization (SEO): Make your article more visible by using SEO.
Your paper, your way: Save time by making your first submission simple.
