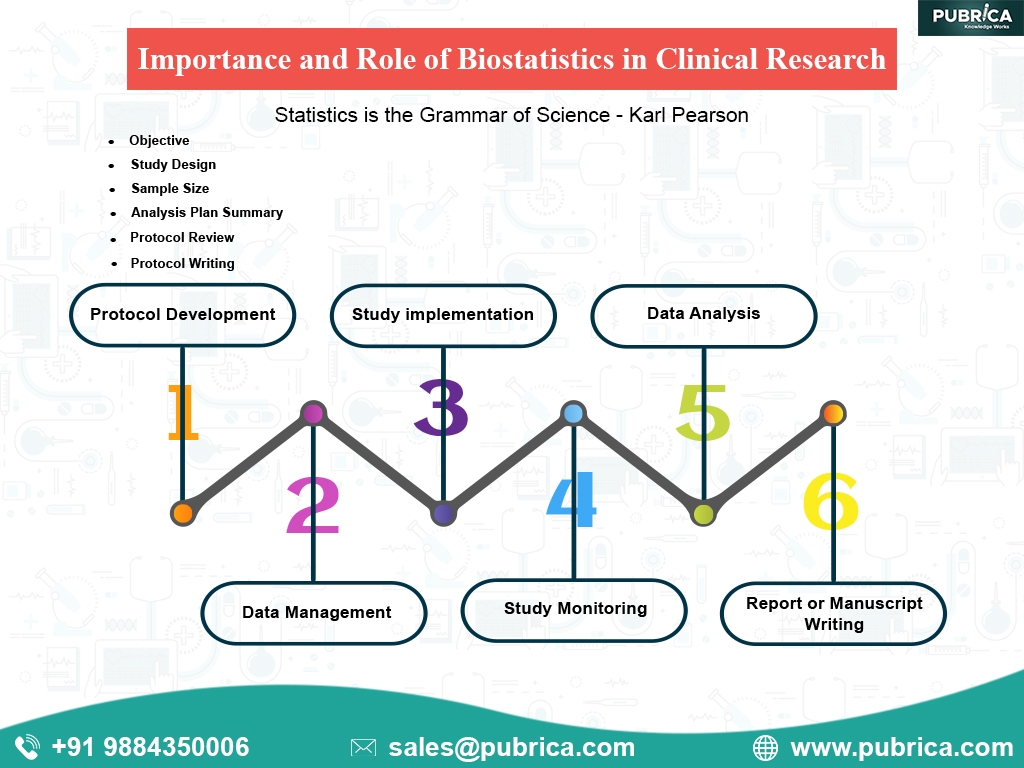
The Importance and Role of Biostatistics in Clinical Research
August 17, 2019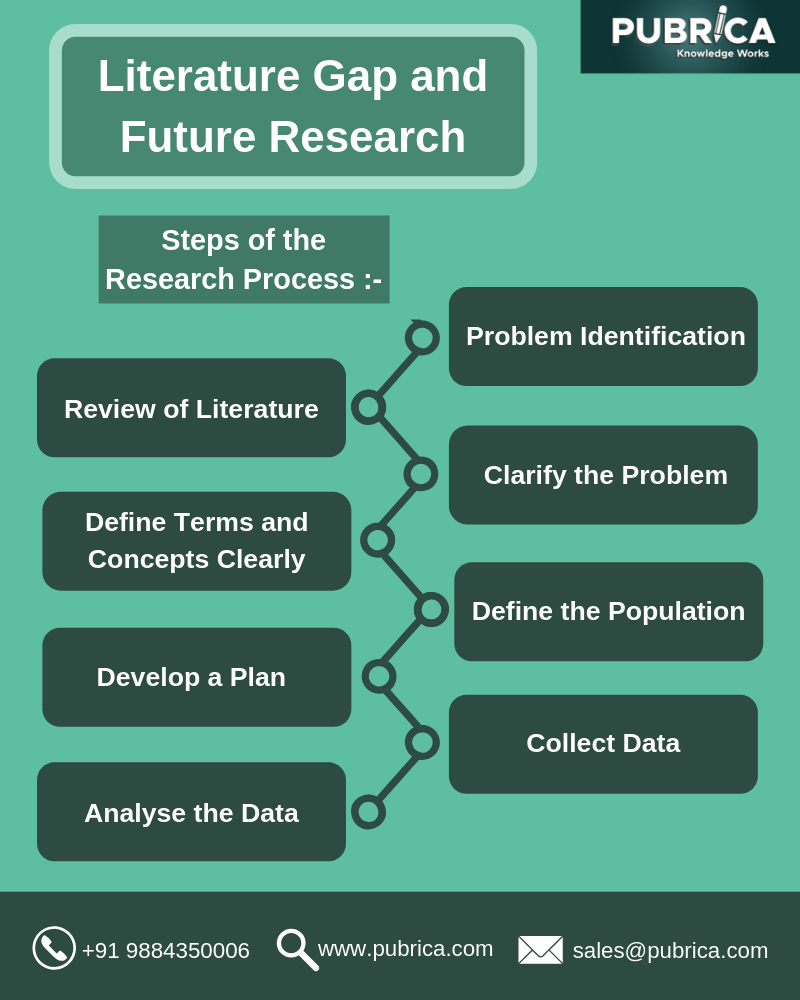
The Literature Gap and Future Research-Research Process
August 24, 2019Statistics dates back centuries working with data collection, organizing and interpreting the data. This was than today we can use statistics to prepare designs, interpreting relations and so on. One of the new developments of statistics over the years has been biostatistics. Biostatistics is the application of mathematical tools of statistics in the fields of medicine, biological experiments and collection followed by the analysis of the data of those experiments and interpreting a relation with the same.
Clinical trials are trials performed on real patients following a fixed protocol. These trials are used to test cancer therapies, the safety of new drugs and treating cardiovascular diseases in humans. These trials help to identify the effectiveness of the drug in different phases which have been broken down in the trial. The clinical trial follows a protocol stating the type of people that may participate in the trials. There are 4 phases in clinical trials:
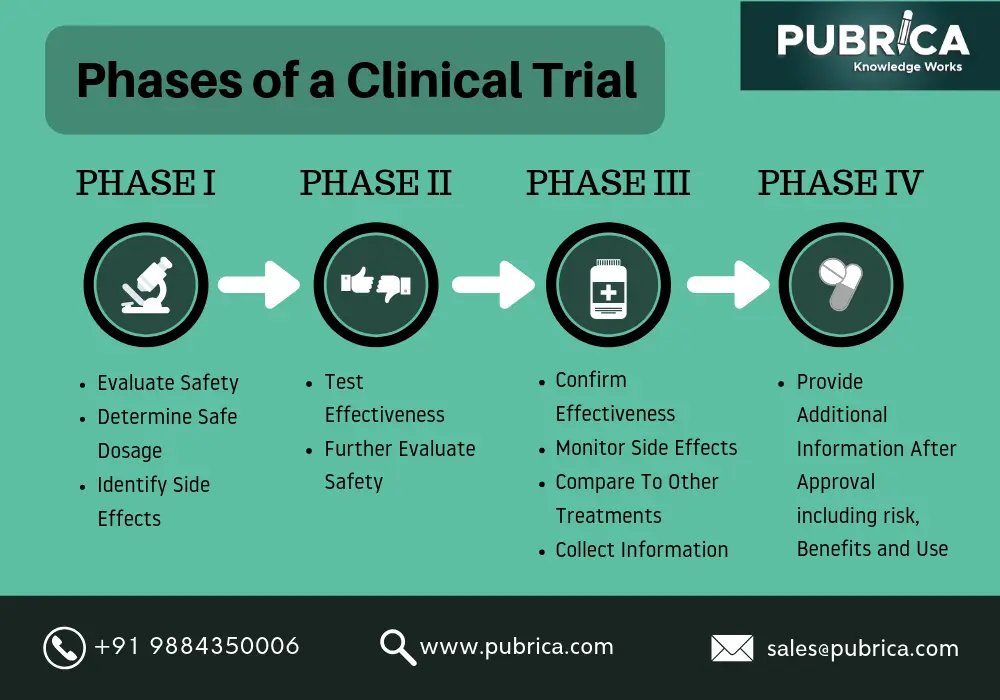
Phase 1 clinical trial: healthy people of about 20-30 are selected and the drug is administered to them to check the working and possible side effects the drug might have on the patients.
Phase 2 clinical trial: Around 100-300 people are used in this phase. This phase works more on the effectiveness of the drug. The aim is to obtain data on whether the drug is effective in diagnosing certain conditions in people or not. It continues working on safety even in this phase but is mostly restricted to checking out on the side effects that the drug might have on the patient.
Phase 3 clinical trial: The number of subjects is usually about 1000-3000 in this phase. It continues studying the safety and effectiveness of the drug but only this time with different populations and dosages. If the drug is approved by the concerned authorities or organization (FDA) after seeing the positive trial results, it proceeds to the final phase.
Phase 4 clinical trial: After getting approval from the FDA the drug is checked on diverse populations for safety and effectiveness.
Most people take part in a clinical trial Analysis because previous medications or treatments haven’t worked. People also join it if there is no cure or treatment for their condition. People who are part of these trials find new treatments even if they are not available in the market. Others join in to help researchers in their studies. Many studies focus on helping healthy people to prevent certain diseases e.g. hereditary diseases.
- Explanation of the trial to the participant followed by gathering more information from the participant.
- Getting a consent form signed by the participant.
- Screening and checking the participant whether he/she qualifies for the test.
- After selection, the participant is scheduled for a baseline visit (first visit). Here physical and cognitive tests are conducted.
- The next step is placing the participant in the control group.
- Any issues or side effects faced by the participant should be reported to the researchers.
- Regularly scheduled visits by the participants at the research centre so the researcher could evaluate the physical, cognitive along with side effects of the treatment.
But why is Biostatics necessary for clinical trials? Well basically like any statistical tool biostatistics help in the collection, analysis and presenting the data. In clinical trials, biostatics helps in making decisions regarding the safety of the drug, population density type of treatment needed, etc.
Helping in understanding the sample size
The sample size is an important aspect of clinical trials. This is where biostatics plays an important role. If the calculations are done incorrectly, the resulting sample may become quantitative research, which is unable to detect the correlation of the outcome variables and the predictor.
There may be many factors that affect the sample size. These factors can be classified as internal and external factors. Internal factors being access to the sample, resources required and experienced personnel required in the study along with technical support. The external factors include the aim of the research and the appropriate sample size and experience in handling the situation.
How can you find whether your findings are significant or not, this is where p-value comes into play. The p-value helps in interpreting your hypothesis and correlate it with the results. If a p-value of ≤ 0.05 is seen then there is strong evidence against the null hypothesis so it is rejected, when a p-value of > 0.05 arises it indicates weak evidence against the null hypothesis and so it is also rejected. A hypothesis that is close to 0.05 or marginally higher or lower can be considered as a good p-value and the null hypothesis is true. However, a p-value of 0.05 doesn’t always make the finding clinically relevant. If the endpoint being studied has an impact on the patient who is under examination then only we can say that the finding is clinically relevant. If the null data is true then there are chances of getting extreme data furthermore complicating the study further.
As diseases and sicknesses evolve medicines need to evolve along as well. The use of statistics mainly biostatistics has helped evolve biological science over the years. Many areas have been researched while a lot of ideas and medicines are still to be researched and biostatistics is certainly the way forward.
Tags:
Biostatistical Programming | Clinical trials | journal Publishing services | Scientific Editing Services | Medical Writing Services | scientific research writing service | Scientific Medical communication service |
Related Topics:
Medical Research Paper Writing
Scientific Literature review writing
