
How to Frame a Theoretical Framework for the Study?
March 25, 2023
How to conduct a systematic review for diagnostic studies with technologies?
April 1, 2023In brief
The QUADAS instrument for comprehensive evaluations of diagnostic accuracy research was created in 2003. As a result of experience, anecdotal reports, and comments indicating places for development, QUADAS-2 was created. This instrument is divided into four categories: patient screening, index test, reference standard, and flow and timing. Each area is evaluated for bias risk, and the first three areas are also evaluated for relevance issues. In addition, signalling inquiries are included to assist in determining the risk of bias in meta-analysis writing services.
Introduction
Many published studies have used the QUADAS-2 tool to assess the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies included in systematic reviews. Here are a few examples:
- Wong et al. (2019) used the QUADAS-2 tool to assess the quality of studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care ultrasound for detecting hydronephrosis in emergency department patients(1).
- Deeks et al. (2019) used the QUADAS-2 tool to assess the quality of studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of screening tests for colorectal cancer(2).
- Hooft et al. (2018) used the QUADAS-2 tool to assess the quality of studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of various imaging tests for detecting lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer(3).
- Zhou et al. (2019) used the QUADAS-2 tool to assess the quality of studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound for detecting fetal anomalies in pregnant women(4).
- Li et al. (2017) used the QUADAS-2 tool to assess the quality of studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of biomarkers for the early detection of sepsis in critically ill patients(5).
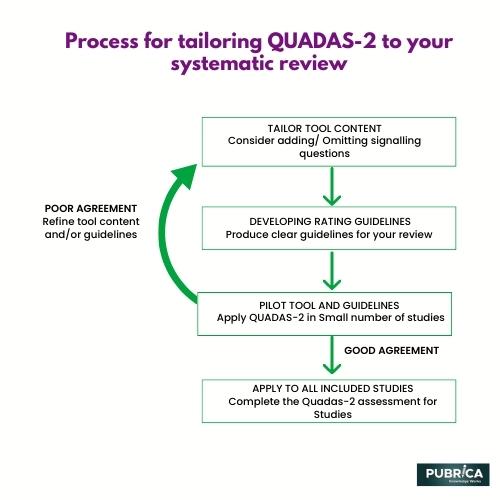
In each of these studies, the authors used the QUADAS-2 tool to assess the risk of bias and applicability of the included studies and to guide the selection and interpretation of the evidence for their research questions.
Conclusion
A complete assessment of the quality of included studies is required for comprehensive evaluations of diagnostic precision studies. Everyone developed QUADAS-2 from the widely used QUADAS instrument using a rigorous, evidence-based approach. The QUADAS-2 tool includes new and improved features such as distinguishing between bias and applicability, identifying four key domains supported by signaling questions to aid judgment on the risk of bias, rating risk of bias and concerns about applicability as “high” and “low,” and handling studies with follow-up as the reference standard.
About Pubrica
The team of researchers and writers at Pubrica creates scientific and medical study papers that can serve as invaluable resources for practitioners and authors. Using the reader to inform them of the gaps in the chosen study area, Pubrica medical writers assist you in writing and editing the introduction. Our specialists are conscious of the order in which the general topic, the issue, and the background are followed by the narrow subject where the hypothesis is stated.
References
- Wong et al. Diagnostic accuracy of emergency department point-of-care ultrasound for the detection of acute hydronephrosis. CJEM. 2019 Mar;21(2):185-193. doi: 10.1017/cem.2018.447.
- Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D’Amico R, et al. Evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of screening tests for colorectal cancer using the QUADAS-2 tool: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019 Apr 10;9(4):e025866. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025866.
- Hooft L, Boer M, Hoekstra OS, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 18F-fluoro-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography in the detection of lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2018 May;28(5):2326-2345. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5139-5.
- Zhou Q, Wu J, Zhao X, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound for fetal anomalies in pregnant women: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2019 Feb 14;9(2):e024611. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-024611.
- Li H, Luo X, Wen J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of presepsin for sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jun;96(22):e7326. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000007326
