Importance of meta-analysis in clinical and medical research
Meta-analysis is a quantitative, formal, epidemiological study method used to evaluate prior research studies to conclude that body of knowledge. A meta-analysis’ results may contain a more detailed assessment of the influence of a therapy or risk factor for illness, as well as other outcomes, than anyone research contributing to the meta‐analysis. Significant work is the analysis of study outcomes for variability or heterogeneity. Meta-analysis has several advantages, including a consolidated and quantitative examination of a broad, often complicated, and even utterly conflicting body of research. Meta-analyses need to identify the result and hypotheses to be evaluated and a careful literature search. Failure to identify the majority of extant research might lead to incorrect findings; nevertheless, there are ways to examine data to discover the possibility of missing studies, such as using funnel plots. Meta-analyses that are meticulously completed are helpful tools in evidence-based medicine. Meta-analytic research is useful because it allows researchers to combine data from several studies, and the massive amount of information presently available makes it possible.
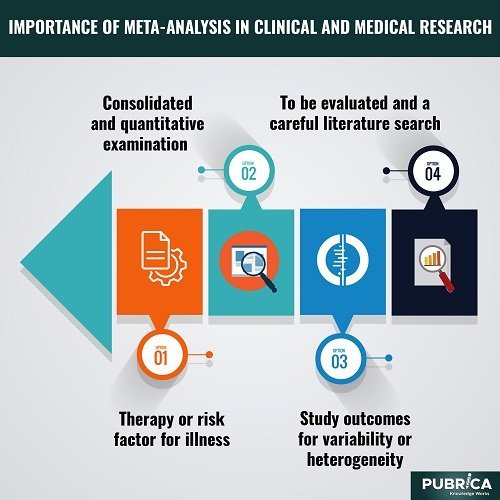
Important medical topics are usually investigated several times, frequently by separate research teams in various locales. In many cases, the findings of many small studies on the same topic are contradictory, making clinical decision-making problematic. The necessity to make judgments that impact clinical practice inspired the movement toward “evidence-based medicine.” Evidence-based medicine may be characterised as a systematic, quantitative, and preferentially experimental method of gathering and utilising medical knowledge. As a result, meta-analysis, a statistical approach that combines the findings of several independent research, is critical in evidence-based medicine.
References
Haidich AB. Meta-analysis in medical research. Hippokratia. 2010;14(Suppl 1):29-37.
