In-Depth Analysis of Recent Cancer Case Reports
May 17, 2024How Meta-analyses have to be Conducted in Medical Research
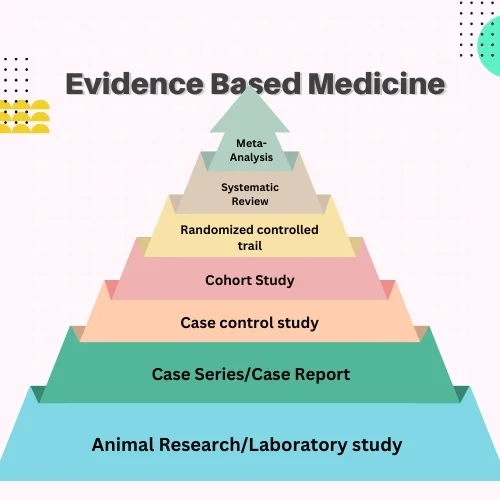
Meta-analysis is a methodical, quantitative approach within epidemiology that evaluates past research studies to draw comprehensive conclusions about the research as a whole. This technique often results in a more accurate determination of the effects of a treatment or risk factor for disease, among other outcomes, compared to the results of any single study included in the analysis. For evidence-based research, combining data from multiple studies (as shown in Figure 1) to draw more precise conclusions, identify patterns, and inform decision-making. In this article, we will delve into the steps to execute meta-analyses for medical research effectively. We’ll explore their approach, methodologies, and best practices to understand how they achieve reliable and insightful results.
What is Meta-analysis and their Types?
Meta-analysis is a statistical technique that combines data from various independent studies to provide a more precise and accurate estimation of the effect size of a particular intervention, treatment, or phenomenon. This approach helps researchers overcome the limitations of individual studies, such as small sample sizes and low statistical power, by pooling data to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the research question. Increasingly popular across many fields, meta-analysis offers a reliable method for synthesizing and interpreting research findings. Various types of meta-analyses include aggregate data meta-analysis, individual patient data meta-analysis, network meta-analysis (NMA), meta-regression, cumulative meta-analysis, subgroup meta-analysis, Bayesian meta-analysis, and meta-synthesis.
Approaches to Meta-analysis
When conducting meta-analyses, rooted in the principles of rigorous research, attention to detail, and a commitment to delivering high-quality results.
| Step | Description |
Step 1: Objectives & Outcome of the research | Clear Objectives and outcome Example Objective: To determine the efficacy of a new antihypertensive drug in reducing blood pressure among adults with hypertension. Outcome: The primary outcome is the average reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Secondary outcomes include adverse drug reactions and patient compliance rates. |
Step 2: Defining PICOS and Inclusion Exclusion Criteria | Define PICOS PICOS Framework:
Inclusion Criteria:
Exclusion Criteria:
|
Step 3: Study Sourcing, Screening, Selection | The initial stage involves identifying pertinent studies that meet specified inclusion criteria. Employs a systematic search strategy, retrieving studies from databases such as PubMed, ScienceDirect, Scirus, ISI Web of Knowledge, Google Scholar, and CENTRAL, complemented by manual searching to ensure all relevant studies are captured. |
Step 4: PRISMA Flow chart | Develop PRISMA (Download Template Figure 2) |
Step 5: Study Quality Assessment | Uses established tools such as the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool or the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale to evaluate the quality of each study included. This assessment helps detect potential biases and limitations within the individual studies. |
Step 6: Data Extraction | Pertinent (patient) information, including sample sizes, means, standard deviations, and effect sizes, is systematically collected from each study. The team uses standardized data extraction forms to ensure consistency and accuracy. |
| Step 7: Data Synthesis | Advanced statistical software such as R or Stata is used to analyze and synthesize data. The team employs various meta-analysis models, including fixed-effects and random-effects models, to determine the overall effect size. |
Step 8: Results Interpretation | The results are interpreted by estimating effect size, confidence intervals, and p-values. A detailed narrative summary of the findings is provided, highlighting the study’s implications and limitations. |
What are the Steps to be Employed?
You need to employ several steps to ensure the quality and validity of their meta-analyses:
Step 1: Collaboration with Domain Experts:
When conducting meta-analysis, you need to closely with domain experts to guarantee that the research question, study selection, and data extraction are both pertinent and precise. Our team ensures that the research questions are well-formulated to meet the study’s objectives, the studies selected for inclusion are relevant to the research question, and the data extracted is accurate and complete while minimizing bias. We prioritize transparency and rigor in our processes to ensure that the research findings are credible and trustworthy.
Step 2: Use of Standardized Tools: The team employs standardized tools, like the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) checklist, that replaced the QUOROM (QUality Of Reporting of Meta-analyses) statement
to guarantee methodological consistency and transparency in their work.
Step 3: Risk of Bias Assessment: Conducts a meticulous risk of bias assessment to detect probable biases in individual studies and adjust the meta-analysis as needed. This includes Cochrane Risk of Bias Tools (randomization process, missing outcome data, deviation from intended interventions, measurement of the outcome, selection of the reported results), Newcastle Ottawa Scale (for observational studies) etc. Bias are assessed based on selection, detection bias, attrition and reporting bias.
Step 4: Sensitivity Analysis: The team conducts sensitivity analyses to assess the strength of the findings and examine the influence of various assumptions and models on the outcomes.
Step 5: Transparent Reporting: Follow a rigorous and transparent methodology in their research, which is reflected in their detailed and comprehensive reporting of the results and limitations. This approach ensures that their findings can be easily replicated and verified by other experts in the field.
Best Practices in Meta Analysis
Several best practices to be adhered in meta-analysis to ensure the quality and validity of their results:
- Practice 1: Registering the Protocol: The team registers the meta-analysis protocol on platforms, such as PROSPERO, to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Practice 2: Using Comprehensive Search Strategies: Use comprehensive search strategies to identify all relevant studies, reducing the risk of bias and increasing the accuracy of the results.
- Practice 3: Assessing Study Quality: The team assesses the quality of each study included to identify potential biases and limitations.
- Practice 4: Using Appropriate Statistical Models: Use appropriate statistical models, such as fixed-effects or random-effects models, to estimate the overall effect size.
- Practice 5: Interpreting Results in Context: The team interprets the meta-analysis results in the context of the research question, study limitations, and potential biases.
Meta-analysis is an effective method to synthesize data from various studies, providing more reliable conclusions in evidence-based research. Pubrica’s team of experts has developed a structured approach to conducting meta-analyses, which involves cooperation with domain experts, utilizing standardized tools, and ensuring transparent reporting. By following the best practices in meta-analysis, Pubrica guarantees the quality and validity of its results, providing valuable insights to clients from various industries. With the increasing demand for evidence-based research, Pubrica’s expertise in meta-analysis is set to play a vital role in driving innovation and informing decision-making.


