Main Manuscript Categories in Cardiovascular Computed Tomography
September 21, 2020
Theories, Tools, and Questionnaires for a Nursing Dissertation Proposal
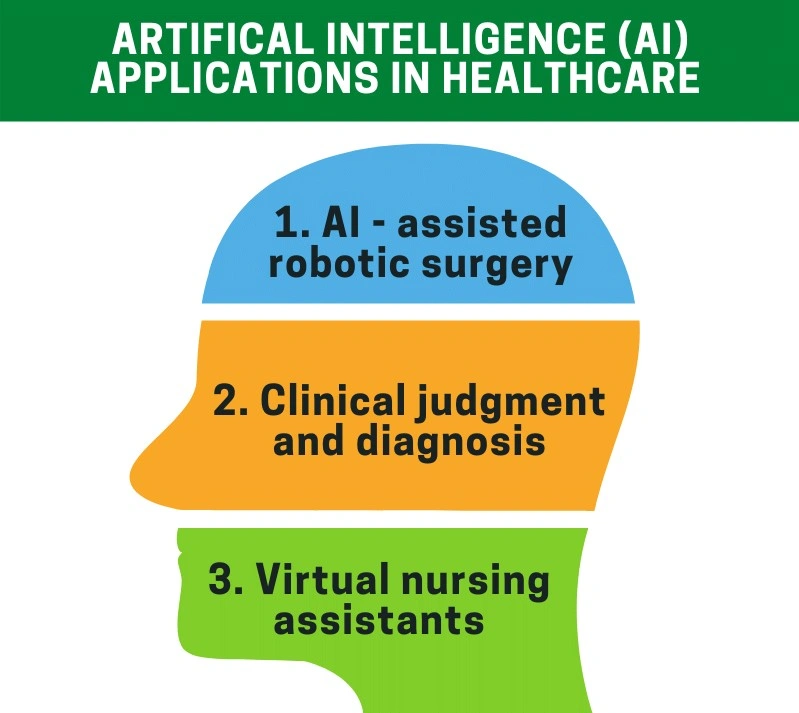
September 25, 2020Artificial intelligence is ruling the digital world by creating new standards in various fields. AI has been creating a greater platform in the field of healthcare development. One of the most important accessibility of AI is to provide information about medical case study report writing to make the data confidential. On the other side machine learning enable the medicos to come up with the best case report writing service. Here are few case studies about the AI paved way to clinical development.
In brief
- Artificial intelligence, machine learning will create a greater platform for clinical development in the future.
- The AI tools will be more beneficial than the traditional methods for detection and to determine how to write a medical case report easily.
- Artificial intelligence is used worldwide for the development in their economy and to create a strong base on their company standards.
Important cases of AI and Machine learning
- AI in cardiology
- Practical implementation in medicine
- AI in global healthcare
- Computer-aided diagnosis
- A translational perspective of AI and machine learnin
AI in cardiology
AI provides all the necessary tools for cardiologists. AI was introduced to face the challenges of performing real-world tasks by providing sociable algorithms. It gives logistic regression which is useful to analyze statistical inference which delivers an algorithm about the basic data, making it difficult for traditional statistical inference. With this more appropriate data, cardiovascular medicine is developed along with case writing services.
Practical implementations in medicine
AI and clinicians work together to formulate more précised medicine. There are few challenges to develop a medicine with this combination. The very first issue is to collect a wide range of data for processing an algorithm. The collected data should be anonymized world-wide and should provide sufficient information. The current clinical unit doesn’t have this wide range of data sharing. Following data collection, transparency is considered. Transparency is done to obtain well-labeled algorithms. Transparency is also an important factor in reinforcing discriminations. This is mainly needed for physicians for the safety purpose of patients and it also helps in writing a case report. Along with that patient safety is another parameter in medicine implementation. The major concern is that patients should not suffer from the adverse effects of using AI technologies. The next big challenge is AI should provide standard data that transform all the obtained data into useful data. AI also assists in building workflow for many streams in the medical field. However there might be some financial challenges in AI implementation in the formulation of medicine, it gives an efficient product than the traditional methods.
AI in global healthcare
Considering the benefits of AI International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) drafted a set of regulations for the safety of people. Many countries have changed their healthcare sectors towards AI and machine learning to develop better standards in their companies. The fastest transition to AI in companies will have a strong base on analysis, visual techniques, imaging sources, etc.
Computer-aided diagnostics
As discussed earlier AI is used for radiology detection. Radiology detection can be achieved by computer-aided diagnosis. ANN is a tool developed by artificial intelligence which is used to detect breast cancer in the form of mammograms. ANN is the algorithmic representation of data (mainly in image processing). The CAD also detects many internal organs such as lungs liver, chest, breats, etc by performing screening examinations. It will be very usefulbfor the radilogists for clinical use and in case study report writing. It is a belief that AI is going to be a major diagnostic tool in clinical developmentent field. The major AI sources will be computer tomography, Artificial Neural network, Positron-emission tomography.
A translational perspective of AI and Machine learning
For the past 30 years, there are no new strategies used in the development of drugs and medicines. This leads to some of the medical errors causing adverse effects to the patients, uncertain regulatory clinical needs, delaying medical reports, lack of information. If the entire process ha changes to AI and machine learning or anything related to computer vision, there will be a greater platform towards much effective growth in innovative techniques in clinical development with an abrupt drug, standardized therapies, improved safety, reducing adverse events.
Some of the changes that took place were,
- Machine learning determined drug discovery targets and molecular compounds.
- Developing a pattern recognition for producing algorithms, available clinical and imaging sets
- To create a multimodel data which provides relevant pieces of information for many particulars.
Conclusion
However AI, Machine learning have subsequently shown growth in the clinical development fields, it is predicted that it will create a benchmark in many companies using artificial intelligence for their research purposes.
References
- Johnson, K. W., Soto, J. T., Glicksberg, B. S., Shameer, K., Miotto, R., Ali, M., … & Dudley, J. T. (2018). Artificial intelligence in cardiology. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 71(23), 2668-2679.
- He, J., Baxter, S. L., Xu, J., Xu, J., Zhou, X., & Zhang, K. (2019). The practical implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in medicine. Nature medicine, 25(1), 30-36.
- Shiraishi, J., Li, Q., Appelbaum, D., & Doi, K. (2011, November). Computer-aided diagnosis and artificial intelligence in clinical imaging. In Seminars in nuclear medicine (Vol. 41, No. 6, pp. 449-462). WB Saunders.
- Shah, P., Kendall, F., Khozin, S., Goosen, R., Hu, J., Laramie, J., … & Schork, N. (2019). Artificial intelligence and machine learning in clinical development: a translational perspective. NPJ digital medicine, 2(1), 1-5.




