Advancement in block chain technology for data sharing in biomedical research – the key factors in writing a literature review
August 7, 2020
Cancer Research Writing: How to Plan and Write a Research Proposal
August 20, 2020In-brief
- Healthcare research is a rapidly growing hey field necessitating the need to do an adequate and comprehensive review of existing literature on the subject.
- Clinical literature review services are in the know-how of writing an effective literature review article.
Purpose of literature review in healthcare research
The whole purpose of research is to increase the collective understanding on the topic and contribute productively.To achieve this, one must begin by understanding the context of the ‘conversation’. And this important task is done by writing a literature review article.
The number of publications, research, and journalsare increasing by the day with an increasing need for dedicated medical writing or literature review services with domain-related expertise. Proportionally the number of rejections is also on the rise. Literature review writing is the first step towards any research and making a clear case for the research study at hand is achieved by a well-done review.Clinical literature review services are providing immense support to busy clinicians and researchers on how to write a literature review. The purpose of a proper literature review can be summarized as below: –
- Literature review help explore previous research conducted in the field of interest, the limitations and conflict areas identified and the need for further research. This justifies the relevance and originality of the research work.
- It also helps one in understanding and formulating one’s area of research in a better manner and justifies the methodology used.
- Literature review article helps connect the statistical findings of the research with prior research statistics.
- It also conveys that the researcher is serious and dedicated about the research and intends to complete the project.
- Literature review writing help is needed in preventing duplication of research and avoiding redundant fields and is needed for good quality research paper.
- Literature review is the preliminary step in any dissertation as part of an academic requirement. How to write a literature review is also an important part of the curriculum.
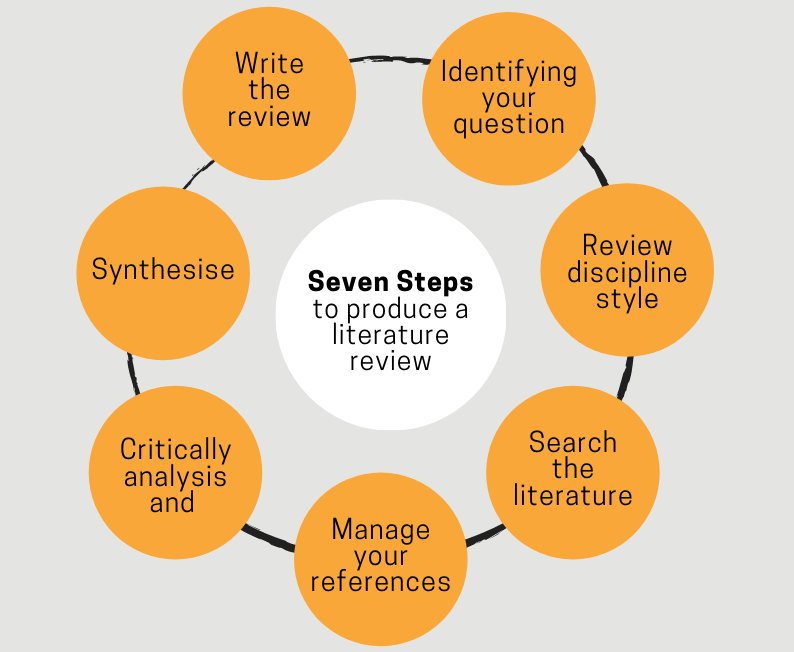
In short, literature review writing is done to place our research within the context of the topic-related existing research and justifies the need for proposed research.
Context of literature review writing
There are various circumstances under which one must do a literature review.
- Introduction to a primary research topic – This sets the context for the research article or dissertation by analysing previously published literature and clearly defining the place of the current research and its contribution to the advancement in the understanding of the topic in question.
- Systematic review –It is related to meta-analysis and provide a quantitative or less often qualitative statistic summarizing several papers.
- Secondary data analysis projects- It is a research project on its own and begins with a clear research question. The project aims at analysing available data in answering the question.
Do’s and don’ts in literature review
Do’s
- The research question should beclear and crisp, preferably one thatcan be analysedquantitatively.
- Picking up the right articles is an art and one should have clear inclusion and exclusion criteria to perform a relevant review.
- Citations should be recent and relevant in the current context.
- Citations should include not only those studies with clear-cut outcomes or inferences, it should also include those that are inconclusive or require further research. This is required for 360 degree understanding, avoiding bias, and defining further scope for research.
- Critical appraisal of the studies cited with an analytical review of the same is to be done.
- Adequate number of citations is often defined by the journal and that needs to be followed.
- Organise and document the data in a format that best suits and justifies the research study.
Don’ts
- Research question should not be ambiguous as it will result in a haphazard start to the research study.
- Deviations or inconsistency in following the defined inclusion and exclusion criteria make the findings unreliable.
- Citations that are old and outdated in the current context are to be avoided.
- Bias in citations that intentionally quote only those that are congruent in their conclusions to the current study should be avoided.
- Not weighing the studies under consideration for the quality of research result in inclusion of poor-quality literature that make the outcomes unreliable.
- Too few or too many citations fail to convey the crux in the correct proportions.
- Data organised in a haphazard manner becomes inconclusive and does not interest the reader and sends a wrong message about the quality of the study.

Basically, depending on the requirement of the topic of literature research, whether it is recent or been around for several years, whether most facts are clear or unclear, whether researchers agree or disagree on most matters and what is the outcome needed out of the literature search in context of the objective of the current study.In short, the review should be well-structured and should have some form to the flow of information.
Some broad guidelines are provided by PRISMA that gives a checklist of 27 items along with flowcharts to help in a comprehensive search.
Conclusion
Setting the factual context of the current research study is the first stepto participate in the ongoing ‘dialogue’ on the subject and contribute positively to that area of research.Literature review services help the busy researcher and how to write a literature review article.
References
- Lingard L. Joining a conversation: the problem/gap/hook heuristic. Perspect Med Educ. 2015 Oct; 4(5):252-3.
- Maggio, L. A., Sewell, J. L., &Artino, A. R., Jr (2016). The Literature Review: A Foundation for High-Quality Medical Education Research. Journal of graduate medical education, 8(3), 297–303.
- Baker, J.D. (2016), The Purpose, Process, and Methods of Writing a Literature Review. AORN Journal, 103: 265-269.
- Christine Susan Bruce (1994) Research students’ early experiences of the dissertation literature review, Studies in Higher Education, 19:2, 217-229.
- Efron, S. E., &Ravid, R. (2019). Writing the literature review: A practical guide. The Guilford Press
- Bollacker, K., Lawrence, S., and Giles, C. L. Discovering relevant scientific literature on the web. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 15(2), 42–47, 2000
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009 Jul 21; 6(7):e1000097.
