- Home
- Insights
- Understanding Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Understanding Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: Definitions, Applications, and Importance
Understanding Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses

Dr.Nancy | Research design and Mixed Methods Research.
30 Jan, 2025

Dr.Nancy | Research design and Mixed Methods Research. 30 Jan, 2025
Introduction
Scientific research articles are broadly categorized into two types: original research articles and review articles. While original research articles report on new studies conducted by the authors and are considered primary literature, review articles summarize existing knowledge on a specific topic, falling under the category of secondary literature. Among review articles, two primary forms are narrative reviews and systematic reviews, each serving a distinct purpose in the research landscape. This article explores the definition and significance of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, focusing on their roles in evidence-based medicine (EBM) [2].
What Is a Systematic Review?
Types of Review Articles
Review articles are classified into two main types [3]:
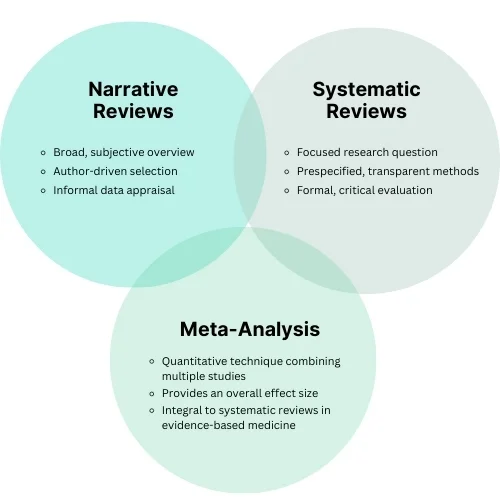
Narrative Reviews (Traditional Reviews):
- Provide a subjective and broad qualitative summary of knowledge on a given topic.
- Conducted by experts who select literature without prespecified criteria or methods.
- Conclusions are based on the expertise and subjective judgment of the authors [4].
Systematic Reviews:
- Offer a structured and comprehensive synthesis of existing research.
- Follow explicit, prespecified methods to identify, select, and critically appraise relevant studies [5].
- Use systematic processes to collect and analyze data, with or without applying statistical methods (meta-analysis)
Definition of a Systematic Review
According to the Cochrane Collaboration (2005), a systematic review is “a review of a clearly formulated question that uses systematic and explicit methods to identify, select, and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect and analyze data from the studies included in the review” [1]. [7]
Key Characteristics of Systematic Reviews
- Focused Research Question: A clearly defined and narrow research question guides the review [1].
- Predefined Criteria: Explicit inclusion and exclusion criteria determine which studies are included.
- Transparent Methodology: The selection process and analysis are documented and replicable.
- Critical Appraisal: Studies are evaluated for their quality and relevance.
- Optional Meta-Analysis: A statistical synthesis may be performed to estimate the combined effect size.
Comparison Between Narrative and Systematic Reviews
| Aspect | Narrative Review | Systematic Review |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad, subjective overview | Narrow, focused question |
| Selection Process | Based on the author’s discretion | Explicit, prespecified methods |
| Data Appraisal | Informal | Formal, critical evaluation |
| Analysis | Qualitative | Qualitative or quantitative (with or without meta-analysis) |
What Is a Meta-Analysis?
Historical Context
The concept of aggregating individual study results dates back to the 17th century, with Blaise Pascal’s pioneering work in probability theory. However, it wasn’t until 1904 that Karl Pearson conducted the first recognized meta-analysis in his study on enteric fever inoculation statistics. In 1976, Gene V. Glass coined the term “meta-analysis,” describing it as “the statistical analysis of a large collection of analysis results from individual studies for the purpose of integrating findings” [4].
Definition of Meta-Analysis
Meta-analysis is a quantitative statistical technique that combines data from multiple studies to calculate an overall effect size or estimate the common effect. This method integrates results from individual studies to provide a comprehensive view of the research evidence.
Contact us today to learn how we can help you navigate the complexities of ethical publishing and prevent plagiarism in your research
We offer the expertise, knowledge, and comprehensive support your Clinical research and publication needs.
Applications of Meta-Analysis
- Psychology and Education: Early applications of meta-analysis were seen in fields like psychology, sociology, and pedagogy.
- Medicine: Meta-analyses have become integral to systematic reviews in evidence-based medicine.
- Guideline Development: They support the creation and revision of clinical practice guidelines by providing the highest level of evidence.
Importance in Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM)
In EBM, systematic reviews and meta-analyses are considered the gold standard of research evidence. They synthesize findings from numerous studies, enabling clinicians and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding patient care. The role of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in EBM underscores their importance in developing robust clinical practice guidelines for managing diseases and conditions [4].
Conclusion
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses are critical tools in synthesizing and evaluating existing research. While systematic reviews employ structured methods to answer specific questions, meta-analyses provide a quantitative synthesis of study results. Together, they form the backbone of evidence-based medicine, ensuring that clinical decisions are supported by the highest quality of evidence. At Pubrica Academy, we guide researchers in conducting systematic reviews and meta-analyses, offering expert support in designing, analyzing, and publishing high-impact studies.
