METAL meta-analysis
In the context of genetics and genomics research, METAL is a commonly used software tool for conducting meta-analyses of Genomewide Association Studies (GWAS). It stands for Meta-Analysis Helper for Epidemiology.
As mentioned earlier, meta-analysis research involves combining data from multiple independent GWAS studies to increase statistical power and improve the detection of genetic variants associated with specific traits or diseases. METAL provides a user-friendly and efficient way to perform such meta-analysis by combining summary statistics from individual GWAS studies.
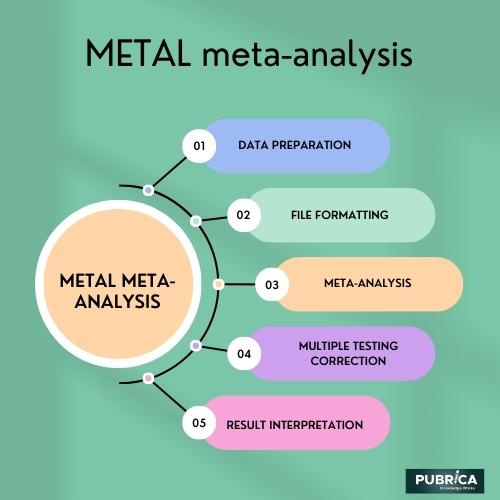
The basic steps involved in using METAL for meta-analysis are as follows:
- Data Preparation: Each GWAS study is conducted independently, and summary statistics for the genetic variants (such as effect size, standard error, and p-values) are obtained for the trait of interest. These summary statistics should be in a specific format compatible with METAL.
- File Formatting: Before running the meta-analysis, each study’s summary statistics files need to be formatted properly. METAL requires all the files to have a common header, and the data should be checked and cleaned for consistency.
- Meta-Analysis: Once the summary statistics files are prepared and formatted correctly, METAL performs the meta-analysis by combining the results from each study using various statistical methods, such as weighted or fixed-effects models and random-effects models.
- Multiple Testing Correction: Since GWAS involves testing a large number of genetic variants, multiple testing correction is essential to control the false discovery rate. METAL can account for multiple testing and provide adjusted p-values.
- Result Interpretation: After running the meta-analysis, researchers can examine the combined results to identify the human genome significantly associated with the trait or disease being studied.
METAL is popular among researchers due to its ease of use, versatility, and ability to handle large-scale meta-analyses efficiently. It allows for customization of the meta-reviewer models and includes options for filtering variants based on various criteria, making it a valuable tool for conducting rigorous and comprehensive meta-analysis in genetics research.
It’s important to note that METAL may not be the only software available for conducting meta-analyses, and researchers may use other software packages or custom scripts depending on their specific needs and preferences. The choice of software often depends on factors such as the analysis’s complexity, the datasets’ size, and the desired level of customization.
References
Willer, Cristen J., Yun Li, and Gonçalo R. Abecasis. “METAL: fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans.” Bioinformatics 26.17 (2010): 2190-2191.
